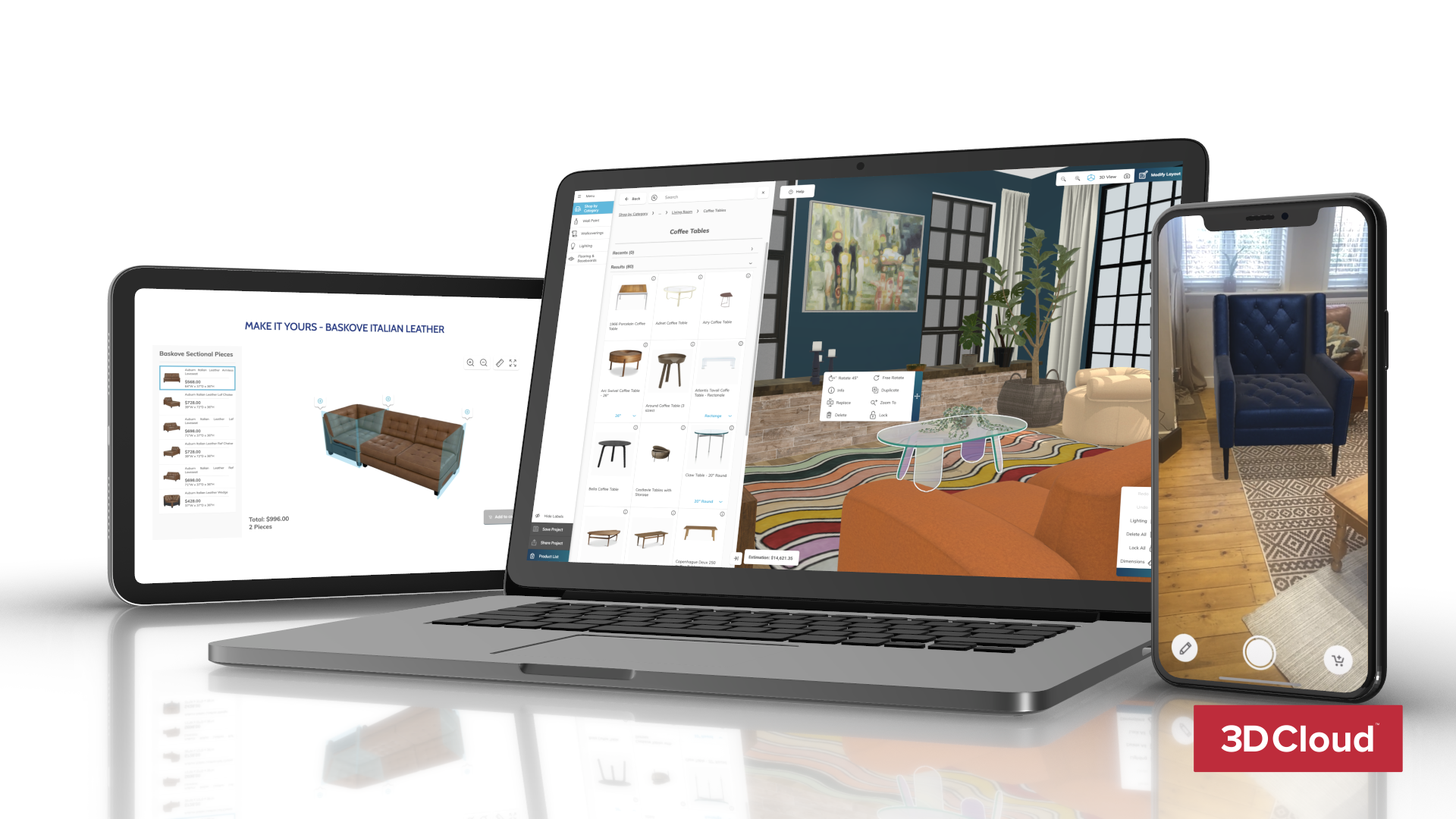
3D e-commerce is becoming the preferred online shopping option for people across the globe. Get the facts and stats about why 3D technology is a must-have for increasing engagement, converting browsers into buyers, and improving market position.
In this article, you’ll find:
3D e-commerce can wow and woo online shoppers. Brands just need the right 3D technology and artistry to start or improve their 3D shopping experience.
What is 3D e-commerce?
3D e-commerce is the integration of 3D models and customer experiences in retail. It includes 3D product configuration, 360 spins, Augmented Reality, virtual try-on, and more. Retailers use 3D e-commerce on product pages, mobile apps, and in stores. The goal: Give prospects and customers interactive 3D product representations and experiences.
3D commerce is also known as 3D eCommerce, 3D modeling commerce, or 3D product e-commerce.
There are many reasons 3D has become a force in online retail, and they all narrow to a single focus: consumers.

Geoffrey Mark, Senior Business and Data Analyst at 3D Cloud and former Director of CGI Strategy and Operations at Crate & Barrel
Geoffrey Mark, Senior Business and Data Analyst at 3D Cloud and former Director of CGI Strategy and Operations at Crate & Barrel, says today’s consumers have high expectations.
“3D eCommerce answers many questions that traditional photography and even the store experience can’t provide,” Mark says.
“Experiencing product scale and in-home stylistic fit through AR, seeing construction details via 360 spins, or bringing unlimited combinations of products or components together visually through configurators and planners can happen long before a customer sets foot in a store. 3D eCommerce can provide both inspiration and validation to drive purchase.”
3D augmented and virtual reality offers convenience and multiple ways to view, try on, and experience items from anywhere, anytime. It allows customers to pre-shop from home. The result is more purchase and brand satisfaction.
How 3D e-commerce works
3D e-commerce combines advanced digital technology with immersive experiences to transform online shopping. Designers and developers build 3D models and embed them on e-commerce platforms. They integrate AR, VR, and customization for consumers to experience products virtually.
Here is an overview of how 3D e-commerce works:
- 3D model creation: Designers craft realistic 3D models of products using specialized software. They construct virtual versions with detailed textures, dimensions, and finishes. These models allow consumers to interact with the product—viewing it from any angle, zooming in on specific features, and rotating or adjusting it to suit their preferences. (Read our Q&A to discover how 3D artists work with 3D modeling.
- Embedding 3D models on e-commerce platforms: After creating the models, developers integrate them into the brand’s website or app. This involves embedding a 3D viewer, enabling customers to manipulate the product directly on the screen. Users explore items in dynamic ways that static images cannot offer—turning, zooming, and experiencing the product in real-time.
- Augmented reality (AR): AR enhances the 3D experience by allowing shoppers to place virtual products in their physical space using their smartphones or tablets. Customers project 3D models into their living rooms, offices, or outdoor environments, seeing how furniture fits, how a pair of glasses looks, or how a product interacts with its surroundings.
- Virtual reality (VR): VR adds another layer of immersion by creating a fully virtual shopping environment. With a VR headset, shoppers step into a virtual store where they can walk around, pick up virtual products, and inspect them as if they were physically present. VR replicates the in-store experience, allowing customers to explore products in an engaging and interactive environment.
- Customization and personalization: Many 3D e-commerce platforms allow real-time product customization. Shoppers adjust product features like colors, sizes, and materials and instantly see changes reflected in the 3D model. This interactive feature increases engagement and helps shoppers feel more confident in their choices.
- Seamless integration across devices: Whether customers shop on desktops, tablets, smartphones, or VR headsets, 3D e-commerce platforms ensure a consistent and smooth experience. Developers optimize for performance, ensuring the interactive features load quickly and run efficiently on all devices.
- Real-time interaction and feedback: Shoppers interact with products instantly, whether they’re rotating a 3D model, testing it in AR, or virtually walking through a VR store. This real-time engagement helps build trust and creates a deeper connection between the shopper and the product, encouraging a more informed purchase decision.
- Data collection for continuous improvement: As customers interact with 3D and VR models, e-commerce platforms gather valuable data on user behavior. Brands analyze which customization options are most popular, how often users switch between AR and VR, and which product views drive the most engagement. This data helps businesses refine their product offerings and optimize the shopping experience.
3D product models for e-commerce
3D product models are digital, three-dimensional representations of physical products that provide an interactive and detailed view of an item. 3D product models serve different purposes depending on the industry and desired interaction level. The most interaction comes with AR and VR, which require high-quality 3D product models.
There are four main categories of 3D product models:
- Wireframe: The most time-consuming modeling category, wireframes are the points, lines, and curves that describe the object’s edges and have no surfaces. Individually drawn wireframe objects are also independently positioned.
- Surface: Surface modeling defines the edges and surfaces of a 3D object. A polygonal mesh defines the surface. The faces of the mesh are planar or two-dimensional. The mesh approximates curved surfaces ,and added modeling depicts curves.
- Solid: Basic dimensional shapes, cylinders, spheres, boxes, cones, wedges, and donuts are the foundation of solid modeling. Complex solids take shape by subtraction, joining, or finding overlapping volumes. Moving a 2D object or rotating it around an axis are other ways to create a solid model.
- Reality capture :Reality capture produces a digital 3D model of a subject, site, or building using photogrammetry—a method that extracts 3D information from photographs or by using static, mobile, and aerial laser scanning.
Read our 3D modeling guide to learn more.
Developing a virtual shopping space
A virtual 3D shopping space allows online shoppers to customize their products, move them around, or try them on. The various types of virtual shopping include view-in-room, 3D product configurators, and more. A virtual experience enables better purchasing decisions.
Here are the main types of 3D shopping experiences with examples:
- View-in-room AR: Consumers try out furniture and décor in different configurations in realistic spaces on a 3D e-commerce website. Major furniture sellers like IKEA and Macy’s provide this tool on their websites.
- 3D product configurators: The potential buyer can change the colors, textures, and other features for all products, from furniture to personal items like Brilliant Earth engagement rings and Converse shoes.
- Visual configuration, price, and quotes: Consumers customize almost every aspect of significant purchases, such as BMW SUV or deck designs from TimberTech. The technology generates a bill of materials and final price, so customization is adjustable to fit taste and price before the final purchase.
- Virtual store: Online customers enter a virtual store, browse the products, and place selections in their cart. For example, Benefit Cosmetics created the grocery-inspired Benemart, where customers can shop with friends and virtually try products. Crate & Barrel created a virtual version of their flagship New York City store. And Walmart created Walmart Realm, a fantastic ‘90s mall filled with its products.
- Virtual try-on: Using their image, buyers can apply makeup from cosmetics companies like Sephora and Dior. They can also try on makeup or clothes from Walmart, clothing from H&M, and glasses from Prada or Warby Parker—just about anything wearable.
- Computer-generated imagery (CGI) for photo replacement: Building the right mood around a product using traditional production is costly and takes time. With CGI, brands let consumers look at product variations—setting, color, texture, uses, and more—without drastically raising costs or time to market.
Types of 3D e-commerce
Websites and apps offer various types of 3D e-commerce, such as 3D visualizations and 360-degree rotations. Other types include real-time interactive 3D, AR, and VR. With 3D e-commerce, consumers can experience products more fully.
The next sections detail each of these types of 3D e-commerce with examples.
3D product visualization in 3D e-commerce
3D product visualization allows customers to see products in realistic spaces like their homes or offices. Shoppers can see product colors, textures, scale, and placement. Viewing in 3D makes it easy for potential customers to know what they are buying.
3D visualization is helpful for more expensive items like home or office furnishings, exterior home improvement products, and appliances that need to fit into a specific space and meet aesthetic requirements.
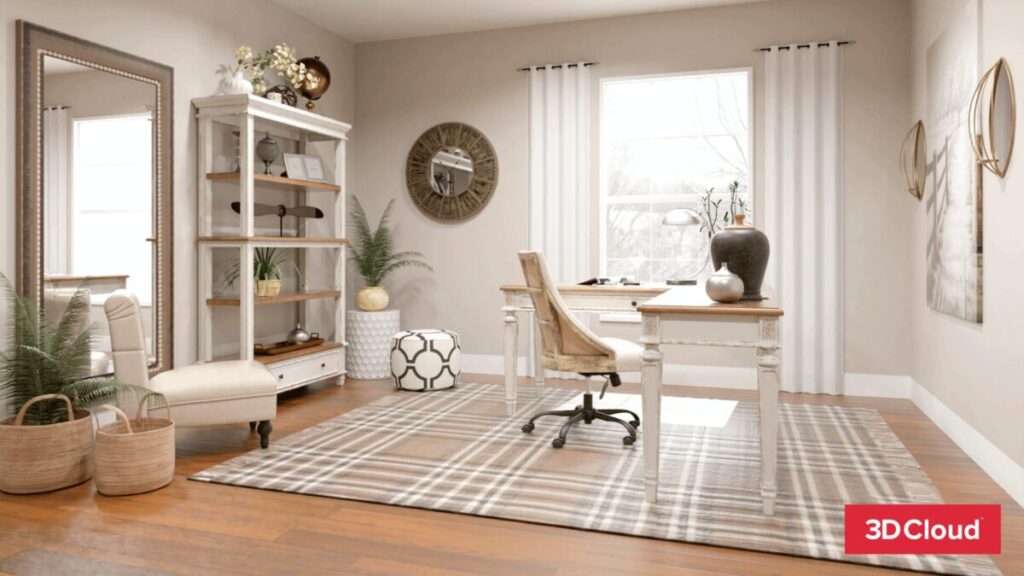

Office Rendering 3D Cloud Office Planner with Design from Photo
360-degree rotations and spins in 3D e-commerce
360-degree rotations and spins in 3D commerce allow customers to examine product details in real-time. They can see items in hyper-detail, rotate, and zoom in and out. This gives buyers confidence and a higher propensity to buy big-ticket items like electronics, cars, and homes.
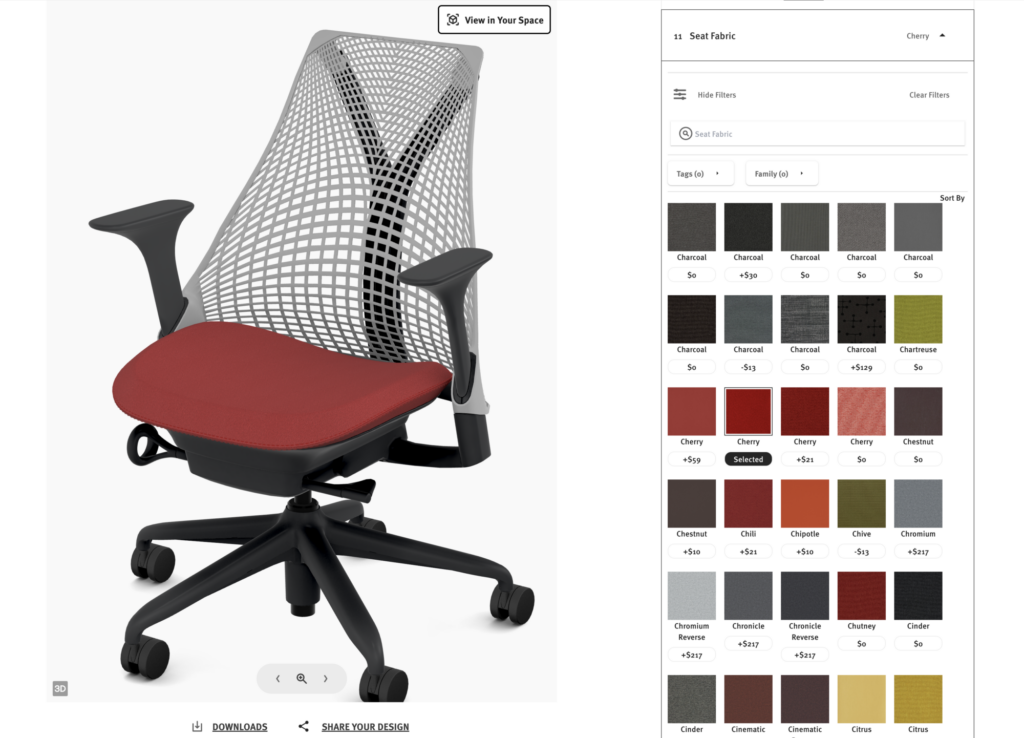
3D Cloud 3D Product Configurator for E-commerce
Real-time interactive 3D accuracy for 3D e-commerce
Interactive 3D connects consumers to the digital world. It allows them to interact with products like in the real world. Experiences range from dynamic web interactions to fully immersive VR, AR, or mixed reality.
Mixed reality (MR) combines the physical and virtual worlds. This technology is an excellent tool for selling complex items like sports cars with custom features, products requiring assembly, or goods that generally come with an owner’s manual for customer self-service.
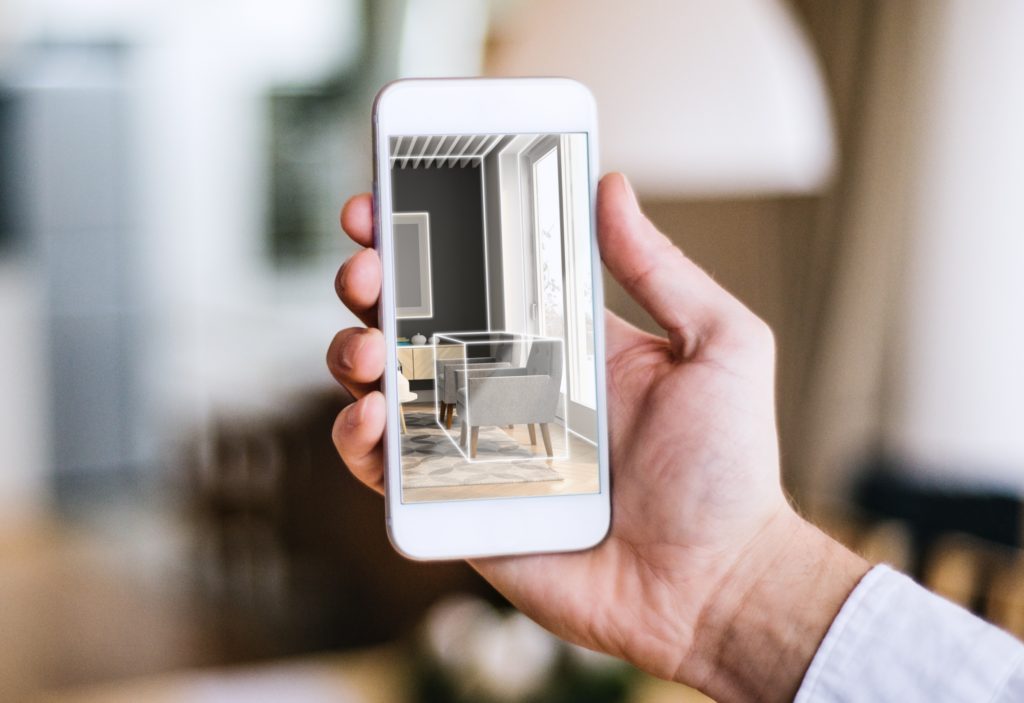

What Is Mixed Reality? | 3D Cloud
Augmented reality for 3D e-commerce
Augmented reality for 3D commerce shows real-life objects enhanced by computer-generated perceptions. AR can engage sight, sound, touch, sensation, and smell, making it increasingly real to consumers.
Shoppers need only a computer or mobile device to experience AR. It requires less equipment than VR, making it more accessible. According to an eMarketer report, 35% of U.S. respondents used AR to visualize vehicle or furniture customizations as of June 2020.
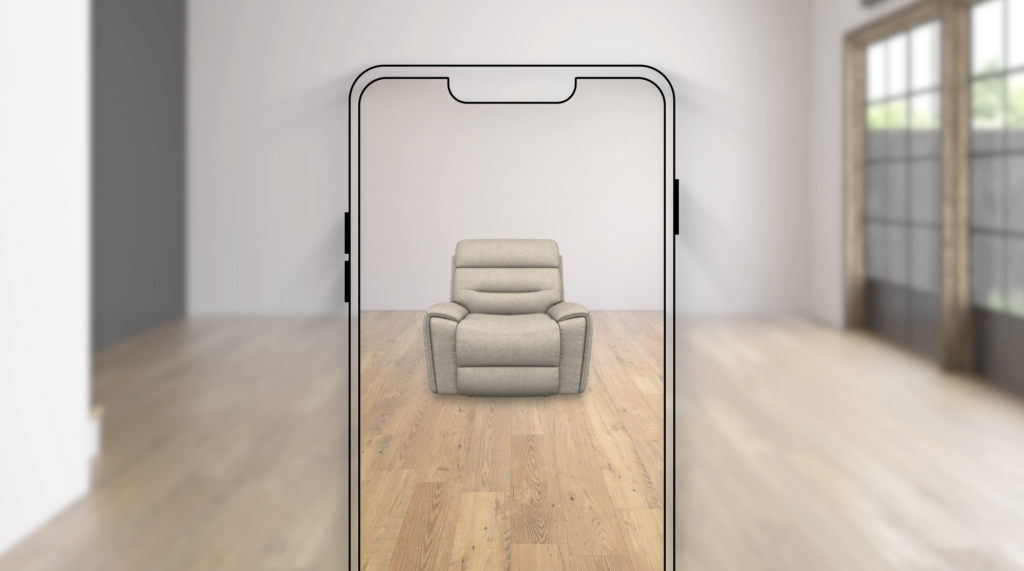

3D Cloud WebAR and Augmented Reality Furniture Solutions
Virtual reality for 3D e-commerce
Virtual reality for 3D e-commerce involves donning a head-mounted display and tracking device. Surround sound adds to the experience.Users can interact with a computer-generated environment in VR. It creates a sensation of shopping in-store without physically being there.
VR equipment manufacturers are racing to refine less expensive, lighter, and more accessible devices. Right now, VR virtual showroom access is both in-store and via devices. Customers can browse through clothing racks, touch and feel all kinds of products, and meet with friends in real time for a joint shopping experience. VR is a profoundly brand-building shopping experience.
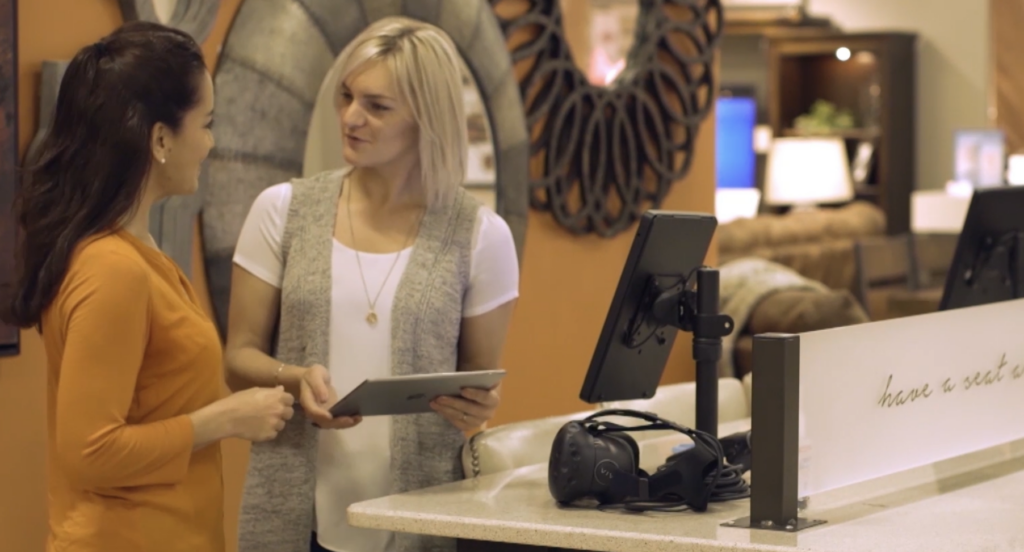

3D Cloud Virtual Reality Shopping Apps for Retailers
Why 3D technology is important for e-commerce
3D technology improves e-commerce for both consumers and retailers. Online shoppers can visualize products better. Retailers can increase sales and customer satisfaction. 3D e-commerce is more engaging and effective.
Consumers appreciate the convenience of learning about products without seeing or touching them. Many customers now expect brands to create shopping experiences that entertain and inform.

Shawn Rothery, Director of 3D Content for 3D Cloud
Shawn Rothery, Director of 3D Content for 3D Cloud, says, “There’s no question that the next generation of e-commerce is 3D. First, there was the internet, then mobile shopping—now it’s 3D everywhere.”
Tony Parisi, a longtime 3D innovator and former Head of AR/VR Ad Innovation for Unity Technologies, adds that increasing realism increases a customer’s satisfaction, even before they buy.
“The more intuitive and real-world the interaction and the more it enables product exploration from all angles, the more it builds a high confidence in purchasing choices,” says Parisi. “And nothing can provide a high production value entertainment experience like real-time 3D graphics.”

Tony Parisi, longtime 3D innovator, formerly of Unity Technologies
3D e-commerce statistics
Statistics show that consumers have embraced 3D e-commerce as it has exploded over the past few years. According to 3D Cloud’s furniture shopping study in 2024, 83% of shoppers considered 3D product configurators “extremely” or “very” helpful. And 65% of consumers prefer to shop at retailers that offer 3D visualization.
The following stats also come from the 3D Cloud Furniture Shopping Trends Study 2024:
- 77% of consumers say using this service makes them smarter shoppers.
- 65% of shoppers who didn’t use 3D tools wish they had.
- 65% of shoppers plan to use 3D visualization for a future purchase.
Mobile devices play a particularly big role in 3D e-commerce.
Pew Research Center states that 90% of the U.S. population owns a smartphone. Worldwide, mobile commerce (m-commerce) accounts for 60% of all e-commerce sales. Based on those statistics, an e-commerce business must keep mobile in mind and ensure that 3D m-commerce is enabled. Take note that millennials and Gen Z-ers spend around 9 hours a day on their phones.
In 2024, Digital Commerce 360 reported that U.S. e-commerce sales grew to about $1.119 trillion in 2023 from $1.040 trillion in 2022 (7.6% growth). According to the Harvard Business Review, AR became essential for online retailers as more people turned to e-commerce during COVID-19. For example, retailers who leveraged AR experienced a 19% increase in customer engagement and a 90% spike in customer conversions, according to a report by Retail Customer Experience.
Benefits of 3D e-commerce for retailers
3D e-commerce offers many benefits for retailers. It boosts sales and reduces returns by helping consumers visualize products. It offers contactless shopping and enhances customer confidence. With AR and VR integration, it attracts more customers, improves conversion rates, and reduces operational costs.
Here are the details on the benefits of 3D e-commerce:
- Attract more customers: People like the fun and engagement offered by 3D shopping. According to data from ecomdash, 63% of U.S. consumers claim their shopping experience would improve with AR. Whether it’s to ensure the fit of apparel or determine the “in place” fit of furniture or appliances in the home, AR and VR work well for customers who want to see products before they buy and have an enjoyable experience at the same time.
- Improve conversion rates: 3D technology increases sales/conversions over traditional methods–sometimes over 40%, according to Cappasity research. Increased sales can help cover the costs of adding 3D e-commerce to a website.
- Inspire customer confidence: Customers must be confident that they’re getting what they want in some luxury categories like jewelry and watches. Overall, online jewelry and watch sales have leaped in the last five years, while higher-end items have seen more modest increases. 3D visuals can help retailers in high-priced categories because customers can take their time, inspect items in detail, and comparison shop.
- Take advantage of mobile: As the world becomes increasingly mobile, having items literally at hand and realistically portrayed offers the ultimate convenience. Consumers can use their mobile devices to view 3D product information or interact with in-store kiosks. They can make product selections and buy while skipping the checkout counter.
- Save time and money: Building a 3D image library is easier, faster, and more affordable than traditional photoshoots. The correct visual presentation can do the work of knowledgeable sales associates and save money on brick-and-mortar personnel. According to SAP’s 2019 Global E-commerce Foundation Report, digital product visualization is about 10% of the cost of conventional photography.
- Keep pace with competitors and big retail: 3D product images bring the shopping experience to a new level that exceeds consumer expectations, which is why top retailers and online malls provide them. Without a 3D strategy, retailers risk falling behind the competition and losing customers.
- Reduce returns: High return rates are usually an issue in e-commerce because the product looks different in person than on the seller’s website. With high-quality images, consumers can manipulate and evaluate products based on real-life specs, eliminating that problem and preventing returns.
- Increase upselling and cross-selling: Tracking customer browsing and buying patterns gives you the information you need for upsells and cross-selling based on known customer preferences.
- Deepen the brand experience: Mixed commerce or interacting with products online and in-store gives consumers a more profound sense of brand allegiance.
With more engagement, higher conversion rates, and fewer returns, mega-retailers like Amazon, Walmart, Target, and apparel companies like Nordstrom, H&M, and Nike use AR and VR as a cornerstone of their overall marketing strategy.
Early entries in 3D commerce include furniture retailers La-Z-Boy and Ashley, cabinetry firms American Woodmark, and kitchen and bath products manufacturers Robern and Kohler. According to the 3D Cloud Furniture Shopping Trends Study, 2024, consumers prefer retailers who offer 3D product configurations, with 72% wanting to use it when shopping for furniture.

Challenges of 3D e-commerce
Keeping up with consumer demands and technology creates challenges in the 3D e-commerce space. Customers increasingly expect immersive and engaging shopping experiences. Businesses must navigate the complexities of integrating 3D technology effectively while staying competitive.
Here’s an overview of 3D e-commerce challenges, including expert insights:
- Pipeline integration complexity
“Our next big step is full integration with digital merchant pipelines,” 3D Cloud’s Rothery explains. “For example, Amazon AR: How do we make our content interact with them directly? Our guiding principle with 3D content is “make once and reuse everywhere,” and that’s the way we are approaching integration issues. 3D Cloud is built for flexibility and adjusts quickly to support the needs of our partners.”
- The need for digital twins
“Companies need to have a strategy right now to create digital twins (3D representations) of everything in their product catalog,” says Parisi. “That’s a big ask, but at some point, that kind of content creation will become commonplace, as ubiquitous as photography. If retailers don’t do it, they will be left behind.”
- Brand storytelling in an AR/VR world
“Companies need to envision how a virtual and augmented world affects how they market and sell their products,” advises Parisi. “Beyond the basic 3D representation of the product, how do you tell your brand story with VR and AR? And how do you provide easy ways for consumers to discover, explore, and try your products in ways that improve the experience of today’s world? The world where digital technology has made buying easy but, in some ways, left the fun of shopping behind?”
- Cost and complexity of 3D content
“The significant remaining barrier to truly having 3D everywhere is the cost and complexity of generating 3D content,” says Rothery. “We’ve overcome other barriers: orchestrating ordering and generation, QA of assets, obligations to multiple platforms, and establishing reasonable standards. We’re already supporting multiple standards, not just file formats like USDZ, FBX, or OBJ–but other 3D content platforms, like Wayfair and Amazon.”
- Large file sizes
3D files are large and can slow down website load times. This can frustrate consumers, leading to higher bounce rates and potential revenue loss as customers abandon their shopping carts. Using techniques such as progressive loading and caching optimizes 3D file sizes.
- Consumer learning curve
Many consumers may be unfamiliar with 3D technology and how to interact with it effectively. This can cause frustration, potentially deterring purchases. Providing intuitive user interfaces, tutorials, and clear instructions can help ease the transition and improve the shopping experience.
- Increased customer expectations
Today’s consumers want personalized shopping experiences, seamless navigation, and quick checkout. Meeting these expectations with 3D e-commerce requires sophisticated technology that integrates personalization algorithms.
- 3D asset consistency
Ensuring that 3D assets look and perform consistently across various devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) is a significant challenge. Creating standardization for assets and implementing responsive design practices can help maintain a uniform appearance and functionality.
- 3D content scalability
As e-commerce platforms evolve, scaling and reusing 3D content becomes critical. This includes integrating new features and content into a management system. Developing flexible, scalable 3D asset management systems that support easy updates and reuse of assets can help manage the growing demands of the platform.
- E-commerce security
Threats such as fraud, data breaches, and financial scams can compromise the safety of transactions. Implementing robust security measures, including encryption, secure payment gateways, and regular security audits, is essential to protect both the business and its customers from potential threats like phishing, malware, and bot attacks.
- Tracking
Tracking how users engage with 3D models—such as rotating, zooming, or changing product configurations—requires advanced analytics tools capable of capturing and processing these detailed interactions. Traditional tracking systems may not be equipped to handle the depth and variety of data generated by 3D interactions.
Examples of overcoming 3D e-commerce challenges
Mark describes these 3D e-commerce pitfalls he has encountered in his career and how his teams overcame them:
- Pitfall: “Underestimating the importance of leveraging standardized 3D model file formats and not jumping into relationships with vendor partners who use proprietary file formats. It’s tempting to jump into the next great technology based on an impressive demo, but time will reveal the shortcomings pretty quickly.”
How we overcame: “We chose to go with partners who were well-versed in standard DCC tools and standards (Autodesk 3dsMax, V-Ray, PBR, WebGL) vs. jumping into game engines or emerging technologies in a big way (Unreal Engine, NeRF, Gaussian Splats). We also forged good advisor relationships with leaders in Khronos Group’s 3D Commerce consortium to ask questions, know the limitations ,and see what was coming next.”
- Pitfall: “Working with 3D modeling resources that would not provide their source models, only optimized versions. This prohibited us from addressing issues on the models on our own or repurposing them as templates for other, similar SKUs.”
How we overcame: “I believe retailers should own their 3D models (source files), and be able to distribute them as they choose. We selected partners that could provide this and avoided model rework costs. We also leveraged this to templatize recurring model needs like mattresses for beds, pillows, curtains, etc.”
- Pitfall: “Not investing in a 3D DAM provider from the start. As models and materials proliferate, the ability to track, store, and distribute them via a cloud-based organized repository can save a lot of internal resource effort. Plus, retailers may not have the IT resources to invest in continuous improvement of these DAMs to optimize workflows.”
How we overcame: “Without a 3D DAM, we essentially had to have extremely organized individuals guiding asset movement, and made sure we had the ability to traffic large batches of models efficiently (Google Drive is not sufficient for this!)”
- Pitfall: “Not having informed, internal technical 3D artist resources to help advise leadership. This is vital, especially if leaders are not well-versed in the world of 3D.”
How we overcame: “My first hires for the CGI department were senior artists (it’s good to have a few, because the opinion of one may vary drastically from another) who helped vet our vendor/partners, assessed 3D model and texture quality, and were instrumental in addressing the hard technical challenges and process definition decisions—it takes time to stay on top of tools to keep quality high and workflows optimized. CGI organization leaders may not have this time.”
Tracking 3D e-commerce performance
Analytics tools can provide valuable insights into a 3D e-commerce site or app. With the right setup, brands can see detailed insights into customer interactions. This can allow you to adjust and improve.
Analytics tool options include:
- Google Analytics: Google Analytics 4 e-commerce tracking is free and offers metrics such as device category, items viewed, items added to cart, and items purchased. For about $150,000 annually, Google Analytics 360 offers comprehensive audit functions, almost 100% accuracy, and data refresh within four hours. This paid version includes data-driven attribution modeling to evaluate online customer behavior.
- Embedded analytics: Some e-commerce platforms have integrated analytics in the backend as part of their solution, providing insights almost instantly.
- Social media analytics: Depending on the e-commerce platform, you can connect your online store to your social media pages like Facebook and Instagram and track the data for further analysis.
- Artificial intelligence analytics: Some tools use machine learning to collect real-time data. They apply it to user data enrichment, user identification across devices, intelligent ad personalization, and predictive analytics.
What should you measure to understand your customer’s behaviors and buying patterns? Here are some metrics to consider:
- Category metrics: Understanding how a consumer engages by category and over time is fundamental to sales success. Other metrics to monitor are visitor repeat behavior, ad performance for retargeting, and the cost of customer service pre-sale. Use this data to evaluate products, promote return visits, and consider category alternatives to offer new or returning customers.
- Qualified sales metrics: These metrics can point the way to upsell opportunities to buyers who place orders after they’ve done their research and made a purchase. You can use these metrics to evaluate conversion over time, per-visit revenue, the size of average orders, and acquisition costs. This information can help you understand a qualified buyer’s persona.
- Post-purchase metrics: Data gathered after a purchase proves that you’re doing things right and highlights areas for improvement. Tracking metrics like rate of return, customer support costs after the sale, buyer satisfaction rates, and the content of customer reviews provide valuable intelligence about brand perceptions.
Analyzing and measuring 3D e-commerce success offers the opportunity to refine product offerings and enrich the customer experience, but it also presents challenges.
3D Cloud’s Mark describes his experience at Crate & Barrel like this:
“Through our e-commerce analytics suite, dedicated analytics team members implemented KPI tracking dashboards. New tools like AR, visualizers, configurators, and room planners may present challenges in establishing direct sales attribution to customer engagement. We looked at the obvious KPIs of engagement/traffic, participation volume, conversion and AOV of 3D tools used vs. not, for signals of improvement. Where multiple categories of products were used, we might look at comparative stats between categories and top performing products to look for patterns.”
Getting started with 3D e-commerce
3D e-commerce starts with a clear vision. Choose products that benefit the most from 3D models, such as products that are visually complex or require detailed visualization. Consider the target audience and how they interact with online shopping, which can influence the product selection.
Mark offers these pro tips for getting started with 3D e-commerce:
- Find key gaps to fill. “Look for customer-enabling, visualization, or customer journey gaps that can help in ways that current photography or online sales tools cannot provide,” Mark says.
- Start small. “Don’t boil the ocean. Start with targeted small pilots to learn and then dial up the volume. Don’t feel like you have to model everything immediately.”
- Start with evergreen products. “great photo references and accurate dimension data; you will learn the process and not be as time-crunched.”
- Don’t obsess over realism. “Be realistic about the limitations of 3D visualization accuracy (photorealism). Not every client context requires it, so pick and choose your battles.”
- Seek quick returns. “Select 3D applications that can deliver immediate value, whether it be image production at scale capabilities or revenue opportunities.”
- Provide engagement tools. “Offer multiple 3D tools that support various levels of customer time engagement—whether it’s simple 360° views, WebAR, configurators, or deep engagement tools like facilitated room planning. Let the customer decide how engaged they want to be.”
- Get a digital asset management (DAM) system. “If possible, a one-stop shop can reduce a lot of administrative work trafficking assets, as well as develop deep partner relationships that essentially extend your team through shared institutional knowledge and common goals.”
- Do a self-assessment. “Assess your own 3D readiness and adjust expectations for delivery accordingly. Make sure the vendors you work with are transparent about the work it takes based on your readiness.” (See 3D e-commerce self-assessment below.)
The next section provides a framework for getting started with 3D e-commerce.
3D e-commerce framework
A framework provides a structured approach for evaluating your capabilities and readiness for 3D e-commerce integration. Use this guide and the self-assessment below to get started.
- Set goals and define scope: Determine what you want to achieve with 3D e-commerce. Common objectives include increasing customer engagement, increasing website traffic, or boosting conversion rates.
- Evaluate current assets and tools: Review the 3D assets and tools that you currently use. Identify what works well and any gaps or areas needing improvement.
- Choose a 3D digital asset management system (DAM): Choose a 3D DAM that aligns with your goals and fits well with your current tools.
- Create naming conventions and metadata standards: Establish these to ensure consistency and easy searchability.
- Implement version control and approval processes: Set up these workflows to manage changes and maintain asset integrity.
- Provide training and resources: Provide training so team members understand the system and processes.
- Integrate into existing workflows: Incorporate your 3D DAM into your current workflows to enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Define access controls: Define access controls so that only authorized personnel can access, modify, or approve assets.
- Establish security measures: Implement backup and security protocols to protect assets from data loss and unauthorized access.
- Monitor and refine: Continuously monitor performance and adjust based on feedback and evolving needs.
- Select a 3D e-commerce partner: Comparison shop and consider features, speed, turnaround time, and integration compatibilities.
- Use a checklist: Download this customizable Excel checklist and comparison chart to track your process and help choose a partner that best fits your needs.
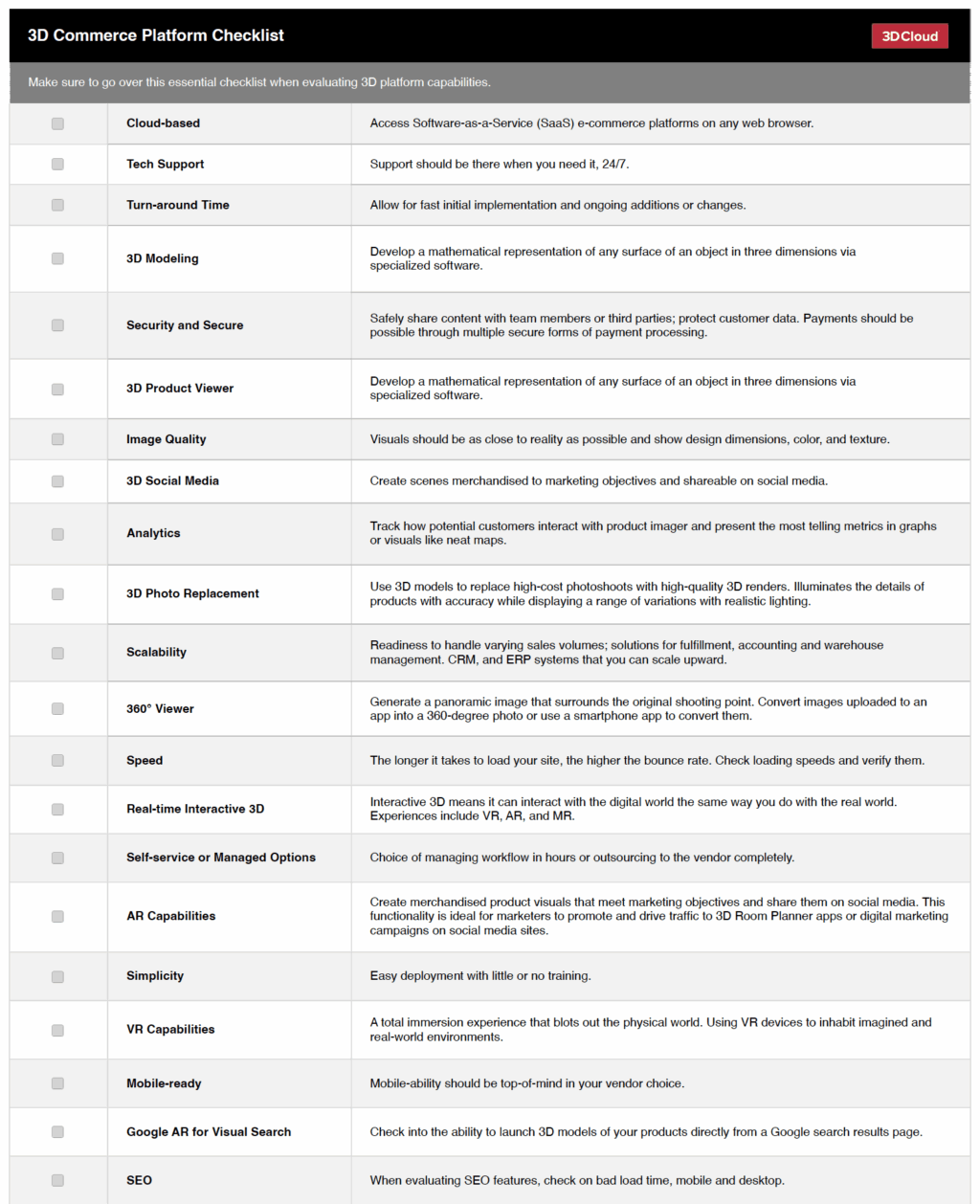
Download this customizable 3D eCommerce Platform Checklist in Excel, PDF and Numbers
3D e-commerce self-assessment
A 3D e-commerce self-assessment should consider the type of products you sell, your competitors, and your budget. Evaluate your overall business and place in the industry to decide if now is the right time to change your visual strategy.
As part of your 3D e-commerce self-assessment, answer these questions:
- Do you sell a product that customers must see multi-dimensionally to understand?
Companies that sell products are often good candidates for 3D commerce. If you are in a service business, the return on your investment may not be high enough to merit the cost of investing in an e-commerce platform and imagery. - Is 3D commerce a cost of entry in your business?
If you sell high-ticket, wearable, or highly customizable products, and your competitors have 3D e-commerce sites, it may be time to shift to higher-quality visuals. - Is 2D holding your business back?
If you have a high percentage of returns, it may be time to move past static 2D images. Boost customer’s product education and engagement before they hit the buy button. - How do your competitors utilize 3D technology?
Analyze competitors in your industry to see if they are leveraging 3D e-commerce. If they are, what advantages do they gain, and how can you differentiate your offerings? - What is your target audience’s familiarity with 3D technology?
Consider whether your customers are comfortable interacting with 3D models. Understanding their preferences can guide your approach and ensure effective implementation. - What resources do you have for creating and maintaining 3D content?
Evaluate your team’s skills and whether you have access to the necessary software and tools for creating high-quality 3D models. - What budget do you have allocated for 3D e-commerce initiatives?
Consider your financial resources and whether they align with the costs of developing and integrating 3D technology, including potential ongoing expenses. - Are you prepared for customer education and support?
Think about how you will inform customers about the new 3D features and provide assistance as they navigate this enhanced shopping experience.
Key elements of implementing or upgrading 3D e-commerce
The same elements of 3D e-commerce apply whether a brand is implementing or upgrading its 3D e-commerce. The components include planning a 3D roadmap, evaluating 3D platforms, site integrations, and more.
Here’s an overview of key elements for 3D e-commerce:
- Digital road mapping: A digital roadmap is a high-level planning document that describes how you plan to meet your objectives for 3D commerce. The roadmap identifies the scale of projects, distribution channels, and digital initiatives. The roadmap can help determine if you need to manage the creative, testing, optimization, and other functions in-house, use a technology partner, or both.
- 3D platforms and vendors: Evaluate 3D platform capabilities. Ask potential vendors for customer references and do some comparison shopping before selecting a 3D e-commerce partner.
- 3D artists and artistry artists use their creative and technical abilities to generate photo-realistic materials, lighting, and rendered images. In VR and AR, believable 3D product models are essential for buyers seeking a realistic product exploration experience. 3D artists are also computer-generated imagery (CGI) artists since that is their medium. CGI artists create special effects, environments, characters, and product renderings.
- Site integrations: Fast-loading 3D commerce sites are essential to a good customer experience. According to a Google study, 53% of mobile website visitors will abandon a page that takes longer than 3 seconds to load. For existing platforms, it makes sense to select a provider that has a current plug-in or app for that platform. Appropriate, scalable integration of AR and VR is vital so that pages load fast to avoid disruptions to customer experience.
- 3D Secure: An essential measure in site integrations is 3D Secure (3DS). It adds extra e-commerce security to protect merchants against fraudulent purchases on their sites.
- Product benchmarking :Start with a practical number of products that already have existing performance data and benchmark against those. A/B testing that uses different variables can improve user flows and a variety of functionalities. The results are helpful for making site improvements and optimizing user engagement.
- Data capture and analysis :There are countless data points around 3D and AR interactions, so be sure to include data capture and analysis. Data capture and analysis measure engagement by category and product, repeat visits, customer service costs, conversion over time, and more. These can help you understand your customers and how they interact with your brand.
Developing a 3D e-commerce strategy
Build your 3D e-commerce strategy around business objectives and measurable goals. A strategy involves more than 3D visuals. It also aligns with your target audience’s preferences and your competitive positioning.
Start by identifying which products benefit most from 3D representation. Then, create a roadmap that outlines technology integration, user experience design, and performance optimization. Analyze competitors and assess customer expectations to fine-tune the content and functionality of your 3D interactions.
Continuously test, gather user feedback, and track performance metrics to ensure your strategy remains effective and delivers ongoing value. When you thoughtfully execute this strategy, you enhance customer engagement and create a lasting competitive advantage.
The next section provides a strategy sheet to guide your 3D strategic approach.
3D e-commerce strategy template
Use this 3D e-commerce strategy template to organize your approach, implementation, marketing, and quality of 3D products. All the essential elements of a 3D e-commerce strategy are included. This structured framework streamlines the development process, enhances team collaboration, and aligns goals.

Download this 3D eCommerce Strategy Template
3D e-commerce best practices
The best practices for 3D e-commerce revolve around customers. Get their feedback as you test your 3D offerings. Use high-quality 3D models to provide a realistic experience. Offer good customer support. Track everything and keep improving.
Here’s a full overview of 3D e-commerce best practices:
- Keep customers top of mind: It’s important to communicate with customers in ways they prefer. Use expectations, buyer demands, and opportunities associated with immersive 3D interactions to elevate their buying journey and ensure conversion and loyalty.
- Test and refine: Set a schedule for continuously testing and refining your 3D e-commerce offerings. Gather customer feedback and analyze interaction data to make improvements.
- Create high-quality 3D models: If your company already uses 3D, find ways to leverage those technologies. If you don’t already have 3D models, start scanning your products or employ a team of 3D artists to create digital twins. In general, scanning is better for small, matte, and opaque products. 3D artists are better for creating larger model goods like furniture and cars.
- Provide robust customer support: Offer comprehensive customer support to assist users with questions or issues with 3D features. This could include detailed FAQs, tutorials, live chat support, and easy access to help resources.
- Ensure accessibility: Ensure your 3D content is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Implement features such as alternative text descriptions for 3D models and ensure compatibility with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
- Monitor and analyze performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your 3D e-commerce features. Use analytics to track user interactions with 3D models, gather insights on customer behavior, and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach helps optimize the shopping experience and increase conversions.
- Follow industry guidelines: Follow industry standards to ensure compatibility, security, and performance. This includes guidelines for model creation, optimization, and user interaction.
Khronos 3D Commerce Industry Group
The Khronos 3D Commerce™ Working Group spearheads industry alignment on 3D content for e-commerce. The non-profit, 170-member group watches over 3D content creation, management, and display. Since the group’s formation in 2000, the use cases for 3D assets in e-commerce have expanded rapidly.
The Khronos standards enable faster playback of dynamic media across a wide variety of platforms and devices. The Khronos Group developed the GLB file format and the glTF file format, which 3D Cloud supports along with other formats.
Industry-wide 3D E-commerce modeling software standards and guidelines
The Khronos guidelines contain best practices and modeling standards. Artists use these to streamline creating 3D models for real-time rendering on multiple delivery platforms. The goal is to provide high-quality 3D assets, AR and VR, product configurators, and interactive 3D marketing tools.
The Realtime Asset Creation Guidelines’ best practices include standards on coordinating systems and scale, file formats and asset structure, geometry, lighting and rendering, materials and textures, publishing targets, and techniques for mapping textures onto 3D assets. See the full list of real-time asset creation guidelines.
The future of 3D commerce from an expert
The future of 3D commerce lies in experimentation. It offers new avenues for consumer relationships, branding, and interactive shopping. Companies will keep improving based on data, new technologies, and consumer needs.
Below, Tony Parisi weighs in on experimentation, innovation, and the role brick-and-mortar locations will continue to play in immersive commerce.
Here are his views on the future of 3D commerce, divided by categories:
- Experimentation and content creation
“In the near term, there will be experimentation around content creation, that is, how to create models of physical products so that we can represent them virtually for use in online catalogs, mobile AR, and virtual showrooms,” predicts Parisi.“For years, 3D content creation was the province of game developers and visual effects experts. But now, every marketer and online catalog manager will need to create and deliver 3D interactive models so consumers can experience products virtually before they buy. This activity will need to scale up fast and be usable by a range of content creators.”
- Innovation in imaging solutions
“There are various imaging solutions in play, including photogrammetry, scanning, converting CAD models, and creating models by hand. They all have trade-offs,” Parisi notes.“Expect to see significant innovation in this area over the next five years. I love what 3D Cloud is doing in this realm because, for many use cases, their platform can procedurally generate 3D models from product data, allowing for infinite variations and great scalability of content production.”
- Enhancing the physical world with computer vision (CV)
CV is the field of study that develops and explores techniques to help computers see and understand the content of digital images, such as photographs and videos.“CV not only recognizes the environment around you so you can place products for viewing—critical for great AR—but also recognizes images and objects, which enhances the physical world with additional information,” explains Parisi.“For example, with certain AR-enabled apps, you can point your phone’s camera at product packaging and reveal additional information about the product or launch entertaining companion content. In the not-too-distant future, this capability will be built into your phone (or some nifty new smart glasses) for pretty much anything and everything in the physical world, not just specific retail products.”
- The role of physical stores
Parisi says brick-and-mortar stores do have a future.“Nothing will ever replace the ability to physically experience products or the personal touch of interacting in the real world with a retail professional,” he says. “Yes, brick-and-mortar are having a tough time at the moment, but we’re starting to see immersive technology employed to enhance the in-store experience. That should increase retailers’ chances of survival.
“Here are some examples of what’s just ahead: AR used to add detailed product information in a virtual space and transforming merchandising into a highly entertaining experience. We’ll also see the use of VR for virtual tours or activities like home planning with the help of an in-store expert. AR and VR will also offer many more items via kiosks or displays than could ever be stocked physically to expand customer choice.”
Examples of 3D e-commerce
3D Cloud has partnered with some of the world’s finest furniture retailers and manufacturers to provide consumers with an upscale 3D shopping experience. Its 3D Cloud® platform is scalable and secure. Here are some of 3D Cloud’s partners and how they use the 3D cloud technology to increase sales.
Raymour & Flanigan 3D e-commerce
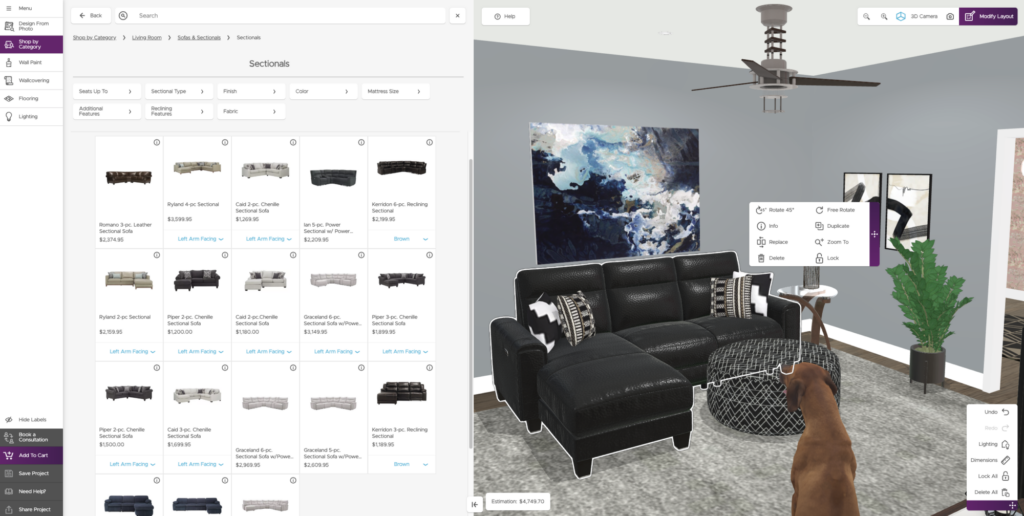
Example of Raymour & Flanigan’s 3D room planner
Raymour & Flanigan Macy’s uses 3D e-commerce to elevate its furniture shopping experience. It allows customers to scan their room with their iOS device and place their selected furniture in it.
TimberTech 3D e-commerce

Example of TimberTech’s virtual deck building
TimberTech uses 3D e-commerce to allow customers to virtually build decking. Customers can choose measurements, configure furniture, specify flooring, set their budget, and more.
John Lewis & Partners
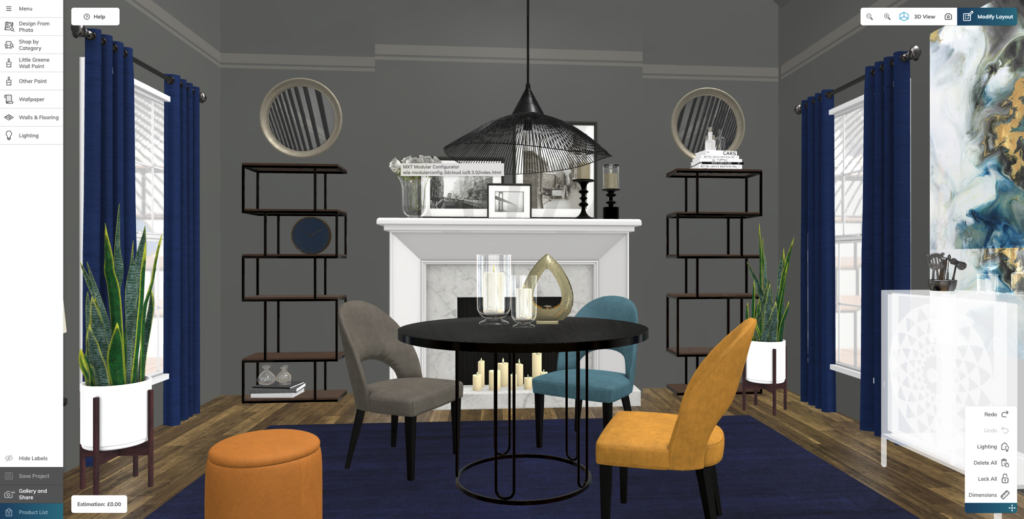

Example of in-room furniture layout from John Lewis & Partners
John Lewis & Partners uses 3D technology for consumers to virtually design rooms within their homes. They can design from inspirational photos, customize colors, and use the drag-and-drop feature to move furniture.
3D Cloud’s 3D Commerce Cloud Platform drives sales
Companies that want to thrive in the competitive retail landscape know they need to provide high-quality 3D experiences to customers.
With 3D Cloud, brands can start or elevate their 3D e-commerce with 3D product configurators, room planners, and more – all from a single 3D digital asset management platform.
Scalable, secure, and proven, 3D Cloud is trusted by leading enterprise retailers and manufacturers worldwide to deliver compelling 3D experiences that convert.
Lowe’s Home Improvement, Herman Miller, La-Z-Boy, Raymour & Flanigan, and American Furniture Warehouse all use the 3D Cloud Platform and 3D Cloud apps to power their 3D e-commerce efforts.










