Businesses can save time, money, and headaches by outsourcing their 3D modeling and rendering projects. This guide explores outsourcing 3D modeling vs. rendering, choosing the right vendor, pricing, and AI’s impact on the field.
Included in this article:
What are 3D modeling services?
Vendors provide 3D modeling services to create and manage 3D content for clients. 3D creators use advanced software and specialized skills to develop realistic portrayals of people, places and things in three dimensions. Clients can outsource this complex work rather than attempting it in-house.

Shawn Rothery, Director of 3D Content for 3D Cloud
No matter what the purpose is, 3D projects generally require a good deal of effort and experience.
“Companies may lack the internal expertise to create 3D content. Or they may find that outsourcing 3D modeling is more cost-effective than building an internal team,” says Shawn Rothery, Executive Director for 3D Cloud.
“Software packages and file types supply varied requirements for realism, resolution, speed, and interactivity,” he says. “Creating 3D content can be challenging to master since requirements can range from the creation of a technical CAD model to 3D game content.”
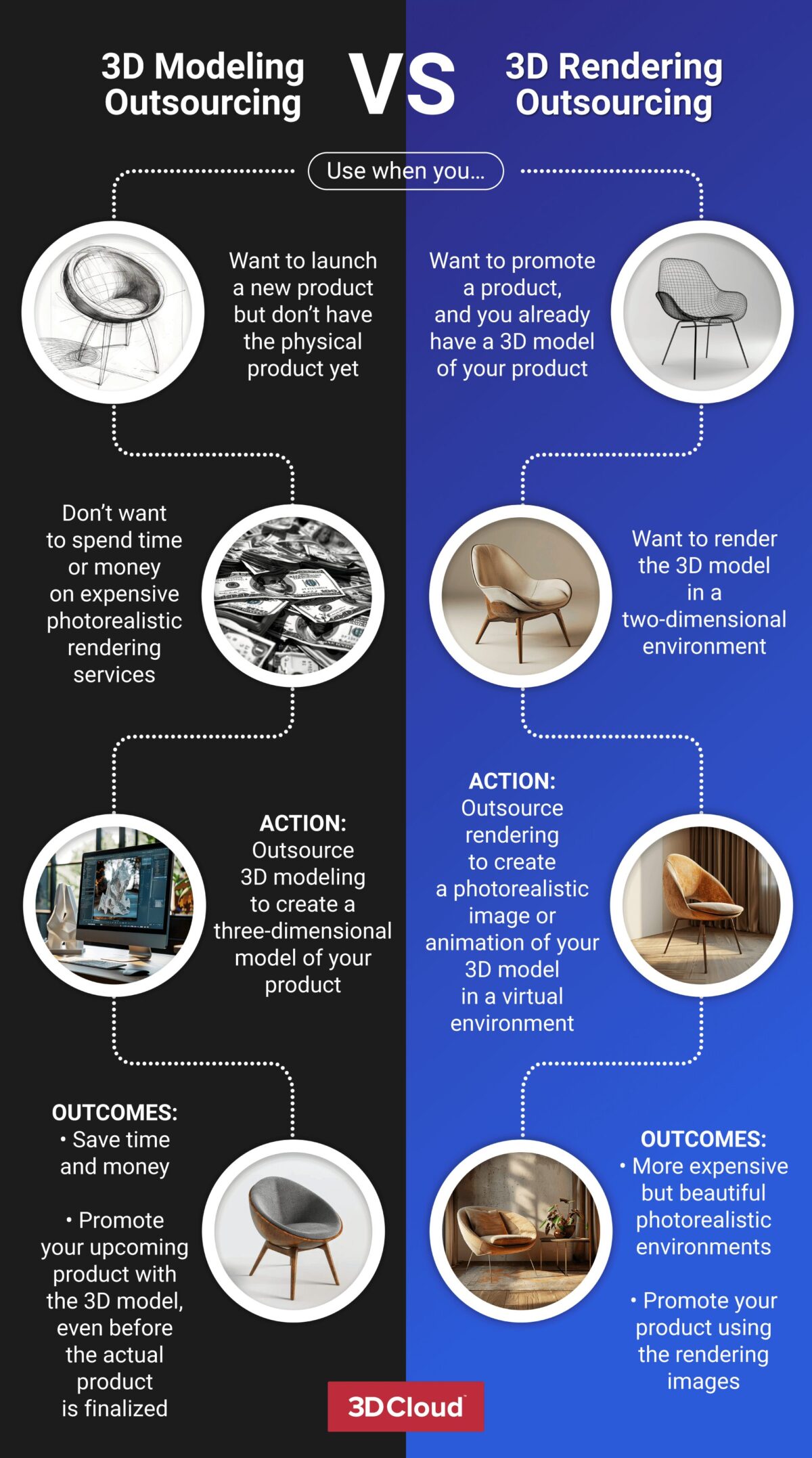
3D modeling outsourcing vs. 3D rendering outsourcing
Outsourcing a 3D modeling project is different from outsourcing a 3D rendering project. 3D modeling involves creating virtual 3D objects, while 3D rendering places those objects in an environment. You can outsource both, but you must already have 3D models to outsource only the rendering.
“A 3D modeling service defines the underlying architecture of a 3D object: the math involved in creating its shape and composition,” Rothery says. “3D rendering services add details like lighting, texture, and animation.”
Rothery describes the 3D modeling process:
“3D modeling includes the use of automated sculpting tools and a suite of curated studios to offload bulk work. After the creation of the 3D model, the content is stored in a CMS [content management system]. Then 3D rendering occurs on the consumption side when an application uses that stored content. The 3D content is served from the CMS to the compatible application, with the CMS rendering based on the use case.”
Then comes the rendering process.
“The rendering takes the basic object and makes it as realistic as possible by adding lighting and shading, while also accounting for speed and performance,” Rothery says. “Also, a model renders differently based on the applications: Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), or spins.”
When should you outsource 3D modeling?
You should outsource 3D modeling if an experienced vendor can do it better or faster than you could in-house. 3D modeling can get expensive either way, so compare the likely ROI of outsourcing vs. in-house. Often, outsourcing provides a higher return on investment.
Here are specific situations when it’s likely best to outsource 3D modeling:
- You do not have a dedicated 3D modeling team in-house.
- You have team members who could do the work but would need to spend significant time learning new skills.
- The quality of your internal 3D modeling resources is much lower than what a specialized firm could complete.
- You have many 3D projects stuck in a backlog and need to get these models done quickly.
- You receive a rush ask, and outsourcing would be faster.
- A 3D model is a one-time project, so it doesn’t make sense to invest in building an in-house team.
The business case for outsourcing is also straightforward: Using an external 3D modeling specialist will save you time—and, therefore, money.
On the flip side, there are benefits to investing in an in-house 3D modeling solution if you have the budget:
- You gain more control of the process and final deliverables.
- Your designs remain confidential.
- You can more easily edit the models as you go and return to the files later if needed.
Ultimately, though, more companies across industries are choosing to outsource 3D modeling services so they can retain internal resources for their core competencies.
Benefits of outsourcing 3D modeling
You get three main benefits from outsourcing your 3D modeling projects. The first two are the quality and speed provided by top vendors. The third is cost savings. 3D modeling can be expensive in-house or outsourced, but you’ll often save money by outsourcing.
“After due diligence to assure quality and reliability of the 3D modeling service provider, outsourcing is typically faster, cost savings are substantial, and operational costs are lower,” Rothery says.
“It’s expensive to build an in-house department from scratch,” he observes. “On top of the modeling team, quality control is necessary—which means you need a QA team on top of the modeling team. It’s often challenging to create a high-performing in-house 3D team depending on requirements. Also, you need a constant flow of content, so their capacity is not wasted.”
Here’s a more detailed list of the benefits of outsourcing your 3D modeling projects:
- Quality: Qualified vendors provide top 3D artists and QA on an ongoing basis to deliver a project that meets your quality standards and requirements.
- Level of Detail: Firms specializing in 3D modeling can produce more detail and precision than an in-house team with less experience and fewer resources. Teams that use AI in 3D modeling will be even more precise, as it reduces the human error of trying to model something exactly.
- Speed: Services enable you to minimize the concept-to-production time. Faster turnaround times result from engaging experienced providers who employ streamlined processes.
- Cost Savings: Rapid turnarounds can save time and money, even on high-volume projects. Ask service providers about competitive pricing and bidding.
- Convenience: Using external resources allows optimization of internal resources, while the right vendor provides superior capabilities based on experience.
- Technology: Take advantage of the latest technologies and file formats in 3D rendering/modeling without investing in them yourself. They will also be deployed by trained and experienced professionals.
- AI Expertise: Top vendors stay current with AI advances now being built into their software.
“Outsourcing 3D modeling provides elasticity,” Rothery says. “Because the capacity of the service is shared, companies receive a high level of talent without having to employ full-time 3D modelers. Companies that outsource pay for what they need when they need it. When you don’t need 3D modeling services, you don’t pay for them.”
Types of 3D modeling to outsource
Companies can outsource any type of 3D modeling project. One particularly common type is 3D product models used in e-commerce and product development. Others include AR/VR modeling and architectural modeling.
Outsourcing 3D product modeling
You can outsource the creation of 3D product models for e-commerce. This allows customers to get a realistic, 360-degree view of the product. That’s a competitive edge that can increase sales and decrease returns. You can use this for clothes, furniture, appliances, or virtually anything.
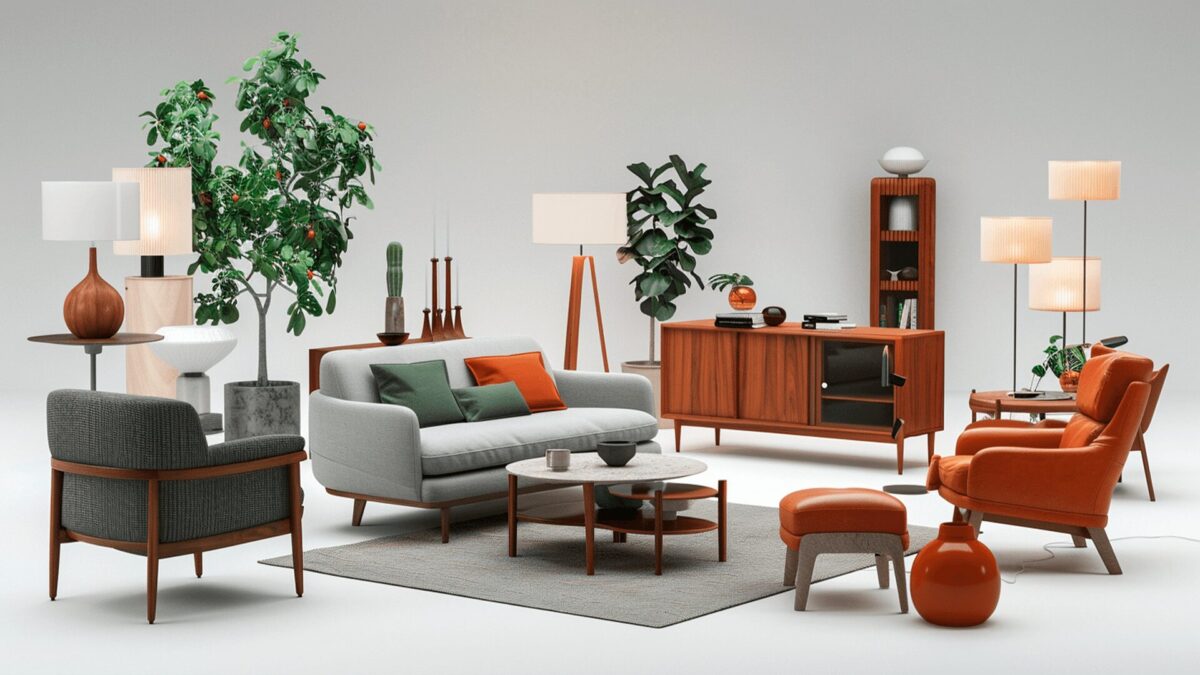

Outsourcing 3D visualization
You can outsource 3D visualizations of proposed products to show stakeholders, investors or clients. Another use case is product development. Stakeholders can grasp changes more readily and reach an agreement.


3D visualization is best for standalone tangible products, such as hardware or devices. If you’re proposing an environment, like a floor plan, it’s best to use rendering. See the section below on architectural modeling for more information.
Outsourcing 3D characters
Video game and animation studios need to create 3D models of the characters before they render them in the actual game or movie environment. They use CGI (computer-generated images) to create the characters. Many games and movies need hundreds of individual character models.
AR/VR modeling outsourcing
You can outsource AR/VR modeling, especially given its complexity. Choose a company that specializes in AR/VR and keeps up with the latest developments. Otherwise, you probably won’t be satisfied with the results.
The models are the same for AR and VR content.
“Let’s say you start with a 3D model of a couch, and you want to view it in VR and via an AR app,” Rothery explains. “You start with a single piece of 3D content representing the couch, around which the client has set parameters for speed and realism. Every 3D model is a compromise between visual quality and speed (often referred to as performance). There’s a sliding scale with realism at one end and performance at the other. The more real a client wants a model to look, the slower it loads.”
In such a new area of technology, standards are still at an early stage.
“In concert with the Khronos Group and the VR/AR Association, we’re developing 3D model specifications,” Rothery says. “We take those specs, generate a single model based on the guidelines, then render it into the best format for delivery to the intended platform.”

Outsourcing Architectural Modeling
Many architectural firms outsource their 3D modeling and rendering. Firms typically do highly technical 2D renderings and then turn to 3D vendors to create 3D visualizations of their work. This enables the architects to remain focused on the design and calculations behind it.
Types of 3D modeling vendors
You can outsource your project to two types of 3D modeling vendors: an established company or a freelancer. Established companies tend to cost more but also have more resources. Freelancers are generally cheaper but may have less experience and support behind them.
Either way, ask about their skills, experience, certifications, references and portfolio of work. Ask specifically about their experience in your field. This may quickly show you the better path.
Outsourcing to established 3D companies
Established companies will have large 3D portfolios that you can look through to get a sense of their style. They also have experience delivering for clients, so while they may be more expensive, they can also be more reliable.
“It can take years for a 3D team to find its footing and deliver high-quality assets,” Rothery says. “The best companies in the field have already created millions of models and analyzed every aspect of the 3D content creation process to find cost efficiencies.”
He sums it up: “If you have an extended timeframe and a big budget, building an in-house 3D team can make sense. For everyone else, there’s hiring an outside provider.”
3D outsourcing to freelancers
Outsourcing to freelancers can present challenges due to a lack of experience, processes, resources, and support. They must not fully understand confidentiality, level of service, or legalities. However, a freelancer with a proven track record might work if you have a tight budget and timeline.
Using AI to do 3D modeling
AI for 3D modeling is in its early stages but is already making a splash. It still requires human intervention to produce a final product, but it will improve vastly in a few years. We’ll see it in entertainment, architecture, gaming, healthcare and other fields.
“AI, and in particular generative AI for 3D assets, is still very early in its emerging development,” says Vince Kilian, Executive Director and Head of Realism for 3D Cloud. “While big advances have been made in the speed and accuracy of very specific use cases recently, the current overall state of the art does not generate a production-ready output without a human in the loop.”
Kilian gives these examples of current AI shortcomings.
“The current solutions have trouble with perspective calculations that result in inaccurate scale and silhouette. These problems are further compounded if there are only one or two angles available of the product,” Kilian says. “When generating the polygon topology for the missing angles, it has to fill the missing information with a prediction of what should be there. These guesses are ‘close enough’ at best and completely wrong at worst.”
That means a human must be in the loop to fix it.
“AI solutions tend to approximate details, hallucinate details and shapes that are simply not present, and require a lot of tweaking and rework to generate something that in the end must still be cleaned up by a human artist during and after the AI-assisted generation component,” Kilian says.
However, he says AI does better in some situations than others.
“For applications that will use a fixed camera and fixed perspective like isometric games, this can still be useful as the player cannot see the other sides of the asset in the game or in the app, and they also typically cannot zoom past a certain acceptable distance,” Kilian says. “With these constraints in place, the current state of AI-generated models becomes a little broader in terms of what can be used in production.”
Kilian quickly adds: “For experiences that require full product orbit and medium to extreme close-ups that do not want to constrain the user’s perspective or zoom distance, these assets quickly fall apart from a quality perspective unless they are manually corrected and refined through a human artist’s workflow.”
This won’t always be the case, though.
“With that said, technology is improving drastically in short periods of time, and I would expect these problems to be resolved within a couple of years for many product categories,” he says, “especially those categories that make up the top sellers for retailers, brands and manufacturers.”
Of course, we will still need humans to give AI directions and check the work. This is especially important when creating work that emulates human behavior, such as creating characters with realistic facial expressions and movement or, on the other end of the spectrum, creating 3D models of products that will appear in global markets and therefore require localization.
Outsourcing to vendors using AI to assist in 3D modeling
There’s a difference between AI-originated products and AI products that are intended to represent real product SKUs. If you’re a retailer or manufacturer outsourcing to a vendor who uses AI in 3D modeling, ask a lot of questions. It’s essential to understand how they incorporate AI and address shortcomings.
“No tool is capable of generating anything other than basic primitive shapes or very specific demo assets that include content that is easily solved by AI in very controlled scenarios,” Kilian explains. “[At least] that would be acceptable for retailers to use at enterprise scale, without the risk of misrepresenting products that AI-generated 3D models are intended to mimic. “
Customers will notice if you accept sloppy AI 3D and pass it on to them.
“Deflating consumer confidence by replacing high-quality 3D assets with subpar AI-generated 3D assets signals to your customers that your brand is willing to relax quality standards to save money,” Kilian says. “It also provides your customers with an inferior user experience, which will certainly tarnish a trusted company’s reputation in the marketplace.”
AI will improve soon, though. “I believe these issues will be resolved for a good portion of the major retail categories in the next three years,” Kilian says.
How much do 3D modeling projects cost?
3D modeling costs vary based on the industry and project scope. 3D modeling costs for products and architecture typically range from $40 to $60 per hour. 3D rendering costs are higher, ranging from $90 to $200 per hour. More experienced talent can charge significantly more.
Vendors often quote pricing by the project, too. For example, architectural modeling projects can cost $400 per room, and 3D rendering projects can cost $300 to $500 for small, one-off projects. That can rise to several thousand dollars, depending on the scope.
“In some cases, AI is being used to accelerate 3D model creation even though it can’t yet replace it. We believe that within the next 3-5 years, content costs will drop substantially, and AI will play a role in that,” Kilian said.
Factors affecting 3D model outsourcing costs
Many factors affect 3D modeling costs. One big one is the project’s scope and complexity. Another key factor is whether you’re outsourcing to a freelancer or an established company. To put your outsourcing cost into perspective, consider your likely return on investment.
Here’s a more detailed look at cost factors for 3D modeling outsourcing:
- Level of complexity and detail: The costs will depend on how complex your model is. Things like texture, lighting, and geometry determine complexity.
- Type of vendor: Established 3D modeling companies will probably be more expensive but have more resources. Companies also have more overhead, while freelancers charge for their time.
- Turnaround time: The faster you need the 3D models, the more expensive it may be to create them.
- Use of existing 3D models: One way to cut costs is to allow the 3D modeling team to use existing, ready-made 3D models of certain objects or components rather than creating originals of everything.
- The contract: How you negotiate the contract is a big factor. Some companies operate under the “on time or for free” guarantee. If they’re late, they will provide the services free of charge.
How to compare and select 3D modeling vendors
Be savvy about selecting a vendor for 3D modeling or rendering. Start by defining your needs and your project. Then compare vendors and ask in-depth questions about their 3D work.
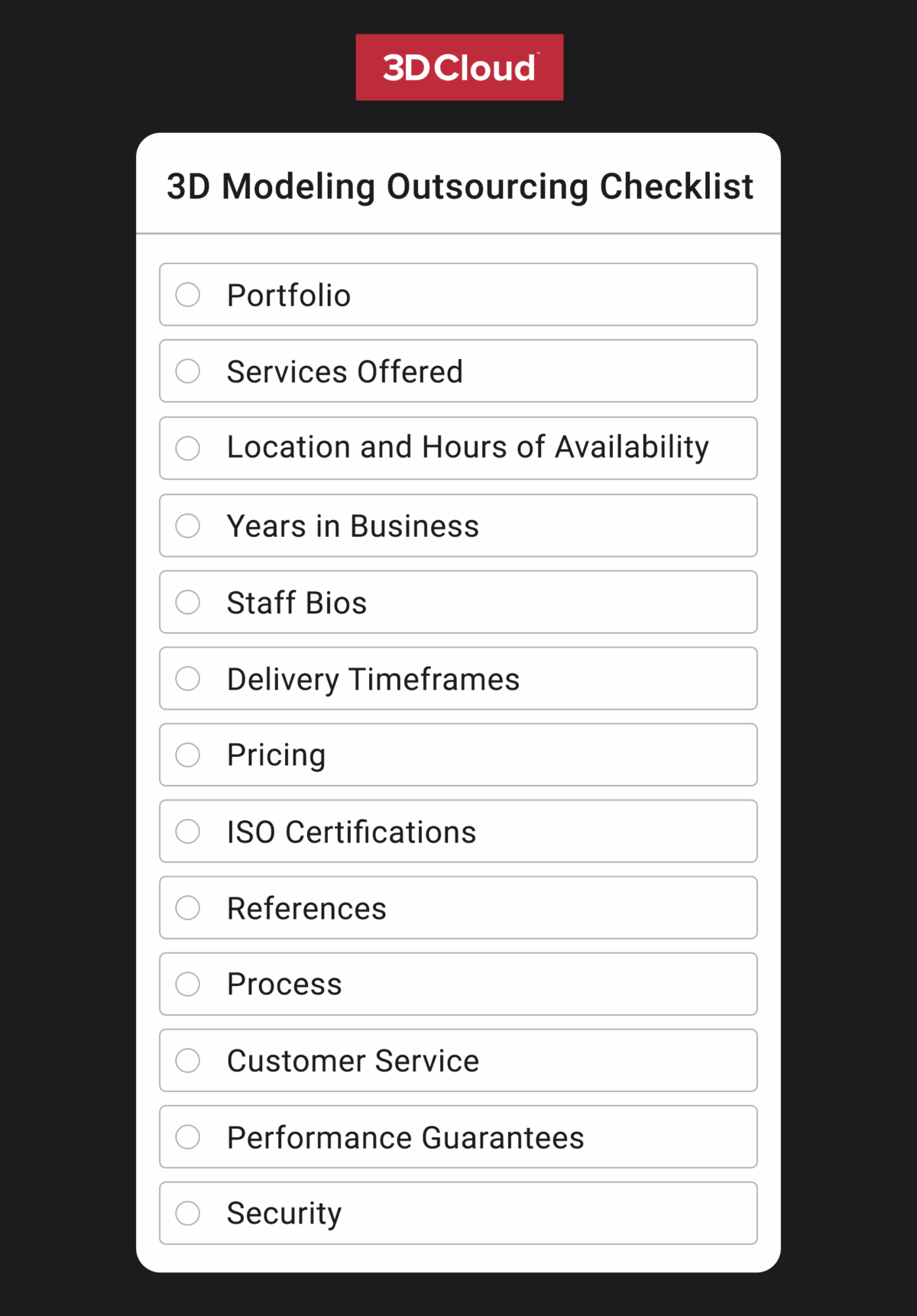 To make sure your questions cover all important items, download our 3D Content Modeling Outsourcing Checklist in Excel, PDF and Numbers.
To make sure your questions cover all important items, download our 3D Content Modeling Outsourcing Checklist in Excel, PDF and Numbers.
Last, determine who best fits your needs and project. Here are more tips on how to compare and select 3D modeling/rendering vendors:
- Ask to see a diagram of their workflow: “Look for a flow diagram of exactly how the solution works end-to-end,” Kilian says, “and ask them to be very clear about the parts of their solution that require human intervention to achieve optimal results.
- Ask how they use AI in modeling: As discussed above, while AI is emerging in 3D modeling, it still poses a number of challenges. Ask the potential vendor how they use AI, if at all, and request any examples of their 3D modeling projects using AI.
“Many of the AI solutions in the market claim to solve problems,” Killian says. “But when evaluated closely, it becomes more obvious that the amazing examples you will see during sales presentations and demos on their website have, in most cases, been modified by a human to get the result shown. If you purchase an AI solution or partner with a provider that claims to have a magic solution, question the total use case and be sure to understand where the solution falls short of consumer and brand expectations of quality.”
- Consider a trial option or project: Kilian suggests this to get important work done while seeing if you work well with the vendor.
- Be wary of generalist solutions: Hiring a vendor in your industry niche is better than hiring a generalist. “Ignore those who claim they can generate anything with precision across a variety of categories today,” Kilian says.
Phases of outsourcing 3D modeling
The first phase of outsourcing a 3D modeling project is defining the project plan. Phase 2 is design when the vendor provides 3D content. Phase 3 is QA testing to ensure everything works. The last phase is the delivery with final adjustments and product launch.
One sign of a reputable firm is a transparent methodology that ensures quality and timeliness, including sharing information about progress over the project’s life. Any prospective 3D modeling vendor should be able to walk you through their process and answer questions before you begin the bidding process.
| 3D Modeling Service Outsourcing Process | |
Definition Phase | |
| Define Scope | The service provider defines the project’s scope, deliverables, budget, and final delivery date in collaboration with the client. |
| Define Plan | The plan is then incorporated into a project plan, PERT chart, Gantt chart, and other formal plan documents. |
| Define Timeframes | Generate and share a schedule. |
| Define All Deliverable(s) | Present the plan for client approval. |
Design Phase | |
| Concept Preparation | Develop, brainstorm, and sketch initial visuals. |
| Create Digital Mockup | Present a mockup to the client. |
| Feedback Fix List | Note input and generate a punch list of items to edit, change, or delete. |
| Refined Draft Deliverables | Finalize changes made per client feedback and present for approval. |
Test Phase | |
| Review Models | Designers and project managers test and review the 3D models and correct bugs and any issues around motion or renderings. |
| Interference Detection | Interference occurs when two 3D entities overlap in 3D space. Run an interference check on existing models to prevent conflicts in the entire model. |
| Validation and Quality Checks | Validation and quality testing ensure the project meets design, development, business, and client requirements. |
Delivery Phase | |
| Clashing Fix | Components of a 3D project often conflict spatially and interfere with each other at a juncture or point. Resolve every clash before finalization to ensure clean imaging. |
| Finalization | Upon detection of inaccuracies in the production prototype of the 3D model and 3D scans, fix the bugs and improve model quality before the final release. |
| Conversion to Desired Formats | A 3D file format stores information about 3D models. The most popular formats are STL, OBJ, FBX and COLLADA. Industries favor specific 3D file formats for historical and practical reasons. |
3D modeling outsourcing in different industries
Companies outsource 3D modeling in many industries, such as advertising, aerospace, architecture, and autos. That’s just the “A” industries. Other popular ones are e-commerce, education, movies, and products.
Industries That Use 3D Modeling Software and Software Services | |
| Industry | Use Cases |
| Advertising and Marketing | Virtual Rendering: Prototypes, products, and packaging can be tested without the high cost of creating new, real products. If projects aren’t accepted, they can be altered virtually. Once the concept is corrected, the rendering can proceed to manufacturing. |
| Aerospace and Aeronautics | Visualization and Prototyping: 3D modeling is becoming essential for the aeronautics and aerospace industries to visualize or order 3D printing for prototyping and production. The software for this industry includes specific features to help deliver mechanical designs that adhere to aircraft safety and reliability standards. |
| Architects | Realistic Interiors and Exteriors: Create these for residential and commercial properties, including virtual walk-throughs and panoramic views. |
| Automotive | Car Design: Programs support 3D design and prototyping of automotive parts, engine redesign, mechanical systems, electronic add-ons, and interior components. Simulations aid in measuring fuel efficiency and drag testing. |
| Building Contractor | Building Information Model (BIM): BIM is a digital representation of a building or infrastructure comprising objects containing dimensions and product information. Objects act in correspondence with one another. For example, when a window placement on a wall moves, the door and location of light switches move relative to each other. |
| Consumer Goods | Product Design: Create products with product engineering, design, and visualization tools that reduce new product development time and help lower costs. |
| Design | Fashion Design: 3D virtual clothing, from basic shirts to elaborate suits, can be created with many options and realistic renderings. Pattern design, fit modeling, and cutting schemes are simplified. |
| Ecommerce/ Retailers | Retail Goods: Buyers view products like apparel, appliances, or furniture from all angles, zoom in and out, or click or tap for more information while considering a purchase. |
| Education | Teaching Materials: Virtual 3D training, simulators, and other teaching materials offer consumers, employees, or students ways to train and learn effectively. |
| Electronics | Electronic Components: As devices have become smaller, electrical components and their mechanical envelopes have also had to shrink. 3D images allow for investigating minute components of a printed circuit board and its integrated system. |
| Engineering | Industrial Design: Designers use 3D software to conceptualize, communicate, and test design intent and aesthetics before building a prototype. Many products, from tablets to headphones to scooters, are designed using 3D software. |
| Entertainment | Movies: Most popular films use 3D modeling. Even in shows that aren’t heavy with special effects, 3D images are frequently added to shots to improve the texture and design of the scene. |
| Gaming | Video Games: Thanks to strides in modeling software and artist techniques, today’s games look less like cartoons and more like live-action movies. |
| Healthcare/Medical | Imaging: From arch supports to prosthetics, 3D scanning, modeling, and printing are improving patients’ lives. Medical imaging also enables better solutions to health issues by examining body structures and systems. |
| Geology and Science | Earth Modeling: Simulations of earthquakes and landforms allow geologists and scientists to see stress effects and develop prediction models. |
| Interior Design | Placement, Color, and Texture: Interior designers use 3D renderings and animations to inform clients and check for design harmony before purchasing. |
| Marine | Weak Point Identification: Evaluation of ship design reveals potential weak points in construction to avoid costly mistakes. |
| Mechanical Engineering | Validation: Mechanical engineers use 3D models to communicate and validate ideas before producing power-producing or power-using machines. |
| Packaged Food | Packaging: Real-time visualization and validation throughout the design process, from concept to production, enable the accurate and fast production of food shrink wraps, cartons, cans, or glass containers. |
| Piping | Operational Safety and Efficiency: Operational safety and efficiency rely on accuracy and design, which factor in conditions like wind, current, seismic loads, and heat. 3D modeling supports the creation of complex offshore structural systems that are compliant with industry codes and standards. |
| Product Manufacturer | Efficiency: Multimedia 3D printing technologies can create an entire floor of 3D printers in place of a traditional manufacturing and assembly line. |
| Publishing | Imagery: The publishing world uses 3D modeling to enhance photographic imagery in illustrated publications such as textbooks. This technology is beneficial for realistically displaying images of flora, fauna, and terrain that are difficult to access. |
| Telecom | Troubleshooting: Engineers can find a broken fiber optic link within a group of cables by holding up a smartphone and opening a specific application. 3D-supported troubleshooting decreases the time to find and fix issues. |
Types of 3D models and corresponding software
Each 3D model type has software options that correspond to it. You might choose MeshLab for a mesh model or Blender for a solid model. Autodesk 3D Studio Max works for a surface model, while Adobe XD is good for a wireframe model.
He’s a detailed look at the types of 3D models and corresponding software.
- Mesh Model: Enables free-form sculpting, creasing, and smoothing capabilities. A 3D mesh uses polygons as the structural build of a 3D model. 3D meshes use reference points on the X, Y, and Z axes to define shapes with height, width, and depth. To make a 3D mesh emulate reality, mass amounts of polygons need to be assembled. Since the shapes are simple, the processing time is faster than with other modeling techniques that already generate smoother curves.
Examples of mesh modeling software include MeshLab, MeshMagic, and Meshmixer.
- Solid Model: This model type employs basic 3D shapes: cones, cylinders, boxes, donuts, spheres, and wedges. More complex solids are created by joining or subtracting the shapes or connecting overlapping volume. Solids are also made by directing a 2D object or revolving it on an axis. Solid models depict an object thoroughly enough to support digital prototyping.
Examples of solid modeling software include Blender, Cinema 4D, Modo, Rhinoceros, and Substance Designer.
- Wireframe Model: A skeletal representation of a 3D object, a wireframe describes no surfaces. Wireframes are composed of points, lines, and curves to define the object’s edges. Wireframe models can be created by positioning planar or 2D objects in a 3D space. Wireframes are useful in the initial product design stages, for design modification and for subsequent modeling,Examples of wireframe model software include Adobe XD, Canva, InVision Freehand, Marvel, and Sketch.
- Surface Model: More sophisticated than wireframe modeling, surface models define the surfaces and edges of a 3D object. The surface modeler defines faceted surfaces using a polygonal mesh. Because mesh faces are planar, the mesh only approximates curved surfaces. Surface modeling enables the analysis and precise manipulation of objects.
Examples of surface model software include Autodesk 3D Studio Max, Autodesk Maya, Blender, Modo, and ZBrush.
A 3D artist needs skill and experience to understand how and when to use the different modeling techniques and software—another reason to rely on qualified services rather than try to bring that capability in-house.
Outsourcing Case Study: Macy’s Adopts a Single-Platform Solution
An immersive 3D experience can lead today’s furniture shoppers to choose your products.
That’s why leading retailers like La-Z-Boy®, Bob’s Discount Furniture®, and Macy’s power their content strategy with3D Cloud Platform, which allows retailers to offer 3D experiences for large catalogs across multiple touchpoints and at scale.
3D Cloud helps customers create 3D room planners, VR shopping apps, AR and VR furniture apps, 3D web AR advertising, and 3D modeling services with one content model rather than needing a separate model for each use case.
Using this “buy once, use everywhere” approach to 3D content, Macy’s offers a few different immersive customer experiences to engage customers in-store, online, and via mobile apps.
Over the past decade, Macy’s has used a combination of AR, VR and 3D room design to help customers visualize their purchases in context before they buy. Customers find it useful to see furniture in their own floorplan before they buy. 3D visualization also helps reduce furniture returns and improve customer satisfaction. The 3D Cloud digital asset management platform for 3D product visualization also supports Macy’s programs like the “Customize It” sofa line, where customers can preview a multitude of covers, colors, and textures before ordering.
Macy’s has dramatically lowered the physical footprint needed to display inventory while enabling customers to see a full selection of furniture, resulting in greater efficiency and profitability.
3D Cloud 3D content modeling services can improve your business
A high-quality 3D experience can wow your customers and help you thrive in a competitive retail landscape. However, building out a 3D content creation team in-house can be expensive.
That’s why outsourcing 3D modeling projects makes sense for many companies. These include top retailers like Macy’s, which uses 3D Cloud-powered 3D product visualization apps to boost sales and reduce returns.
3D Cloud is a smart choice for any furniture or home improvement retailer or manufacturer that wants to build a catalog of 3D models for use in a variety of immersive product experiences. The 3D Cloud Digital Asset Management Platform for 3D Product Visualization is a scalable, secure platform that allows you to store and manage all 3D assets and associated metadata in one centralized place.
“3D Cloud specializes in real-time, highly configurable, and customizable 3D content to engage customers and showcase merchandise,” says Shawn Rothery. “It would be difficult for an in-house team to generate complex projects like room and space planners, configurators, spin renders, and photo replacement without custom software and experienced 3D artists.”
3D Cloud simplifies this process so you can scale, integrate, and reuse components, and focus on the work that matters most.
Learn more about 3D Cloud-powered 3D product visualization apps.